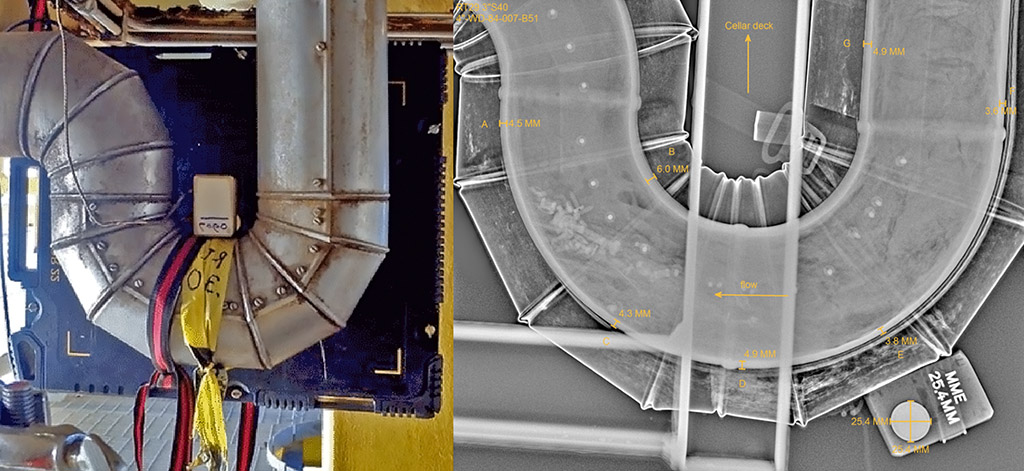
Digital Radiography
Digital radiography is becoming for widely used with advances in digital technology. DR is used for detecting defects, corrosion, erosion, cracks and loss of structure thickness.
Digital Radiography is used for assessing piping, pressure valves and vessels. Digital Radiography techniques can detect discontinuities in a range of materials including composites, plastics, steel and aluminium.
Digital Radiography is similar to conventional radiography, but it doesn’t use traditional film to capture images. Instead, images are captured using phosphor coated imaging plates or flat panel detectors.
An image detector has an X-ray beam focused upon it. The structure that needs to be examined is in front of the detector. As the X-ray beam passes through the structure and hits the detector, it is filtered by the scintillator.
The scintillator comes in different substrate materials such as Cesium Iodide or Gadolinium Oxysulphide. Light emitted from the scintillator due to exposure of the X-ray beam is deflected by a mirror on to a lens. The light is converted to a digital output signal which is read out by thin film transistors or fibre coupled charge device.
Two types of Digital Radiography are commonly used:
- Computed Radiography (CR): makes use of phosphor-coated imaging plates to capture images
- Digital Radiography (DR): makes use of flat panel detectors to capture images
Inspectors can provide companies with instant reporting and digital images allow for data sharing easily. Often images are emailed or sent to off-site experts for simultaneous evaluation. Since the images are in a digital format, they can be archived electronically to be stored, traced and viewed. Digital Radiography does not store images on film, so physical storage space is saved that would normally be required for conventional film.
Another benefit is that costs can be controlled as digital radiography is not subject to fluctuating film costs as conventional radiography is.
Radiograph testing
Advantages
- Information about depth of defects
- Suitable for complex structures and different materials
- Large scale inspection
- Full coverage in short time
- 2D and 3D images
- Good contrast sensitivity
- Manual operation and expensive
- Double sided access is required
- Difficult to use on rotating blades
- Health and safety risks
- Relies on regular inspections
- Short-term field inspection
- Supervision is needed